reading-notes
Stacks and Queues
Stacks
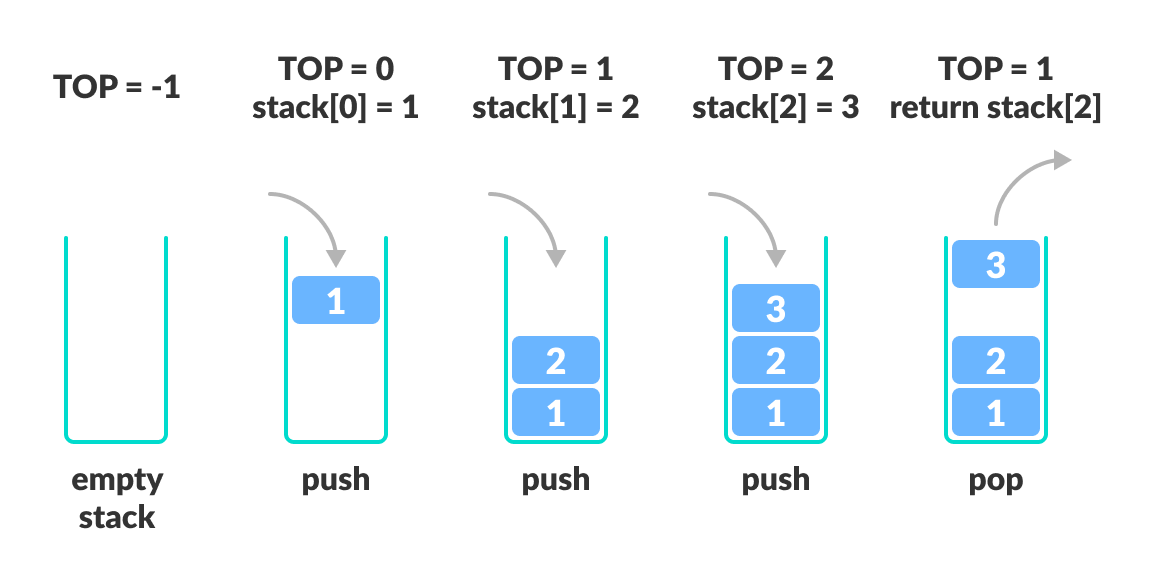
A stack is a linear data structure that stores items in a Last-In/First-Out (LIFO) or First-In/Last-Out (FILO) manner.
FILO Concept
This means that the first item added in the stack will be the last item popped out of the stack.
LIFO Concept
This means that the last item added to the stack will be the first item popped out of the stack.
Stack methods and operations:
- Push : adds node to the stack
- Pop: remove nodes from the stack
- Top: top node of a stack
- Peek: top node’s value in a stack
- IsEmpty: returns a boolean (true: when the stack is empty)
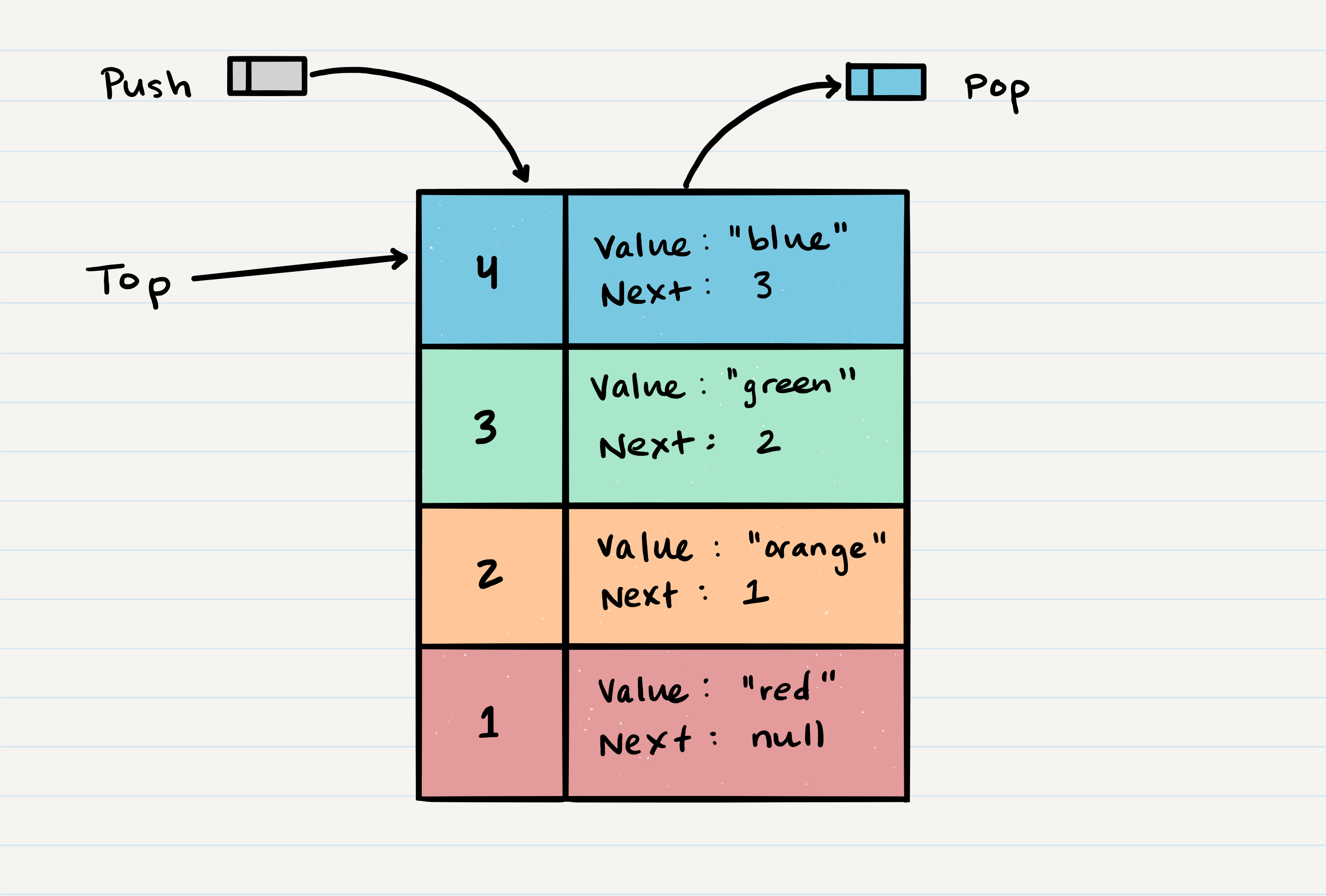
Stack Visual
the picture above shows the structure of a stack,the top is last node pushed into the stack and the first node that would be popped out, if it’s popped out, the top of a stack will be top.next
Stack methods and time complexity
Push
pushing a node into a stack will always have a constant time complexity or O(1), because it will always take the same amount of time no matter what
Pop
pop also has a constant time complexity, because you will always remove from the top, there is no loops.
it’s always better to check if the stack empty by using isEmpty() method before using pop, so an exception will be raised if there is no nodes to remove in the stack.
Pseudo code for pop
ALGORITHM pop()
// INPUT <-- No input
// OUTPUT <-- value of top Node in stack
// EXCEPTION if stack is empty
Node temp <-- top
top <-- top.next
temp.next <-- null
return temp.value
### Peek Method
peek returns the value inside the top of the stack Typically, you would check isEmpty before conducting a peek. This will ensure that an exception is not raised.
Pseudo code for peek
ALGORITHM peek()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- value of top Node in stack
// EXCEPTION if stack is empty
return top.value
### isEmpty method
the time complexity for this method is O(1) // constant
Pseudo code for peek
ALGORITHM isEmpty()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- boolean
return top = NULL
How can we implement a stack in Python?
*there are two ways for implementing stack in python, which are:
- Using the built-in List data structure. Python’s built-in List data structure comes with methods to simulate both and operations.
- Using the deque library which efficiently provides stack and queue operations in one object.
Queue
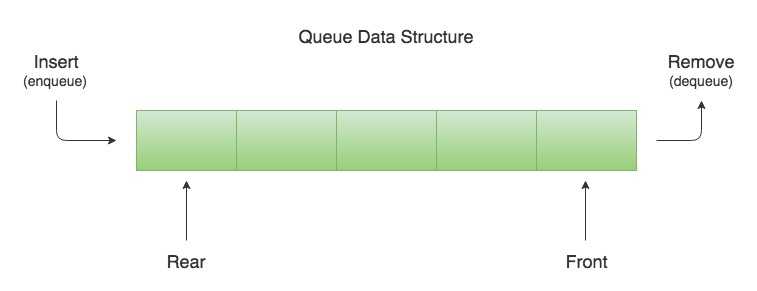
queue is a linear data structure that stores items in First In First Out (FIFO) manner. With a queue the least recently added item is removed first.
Queue concepts
FIFO
This means that the first item in the queue will be the first item out of the queue.
LILO
This means that the last item in the queue will be the last item out of the queue.
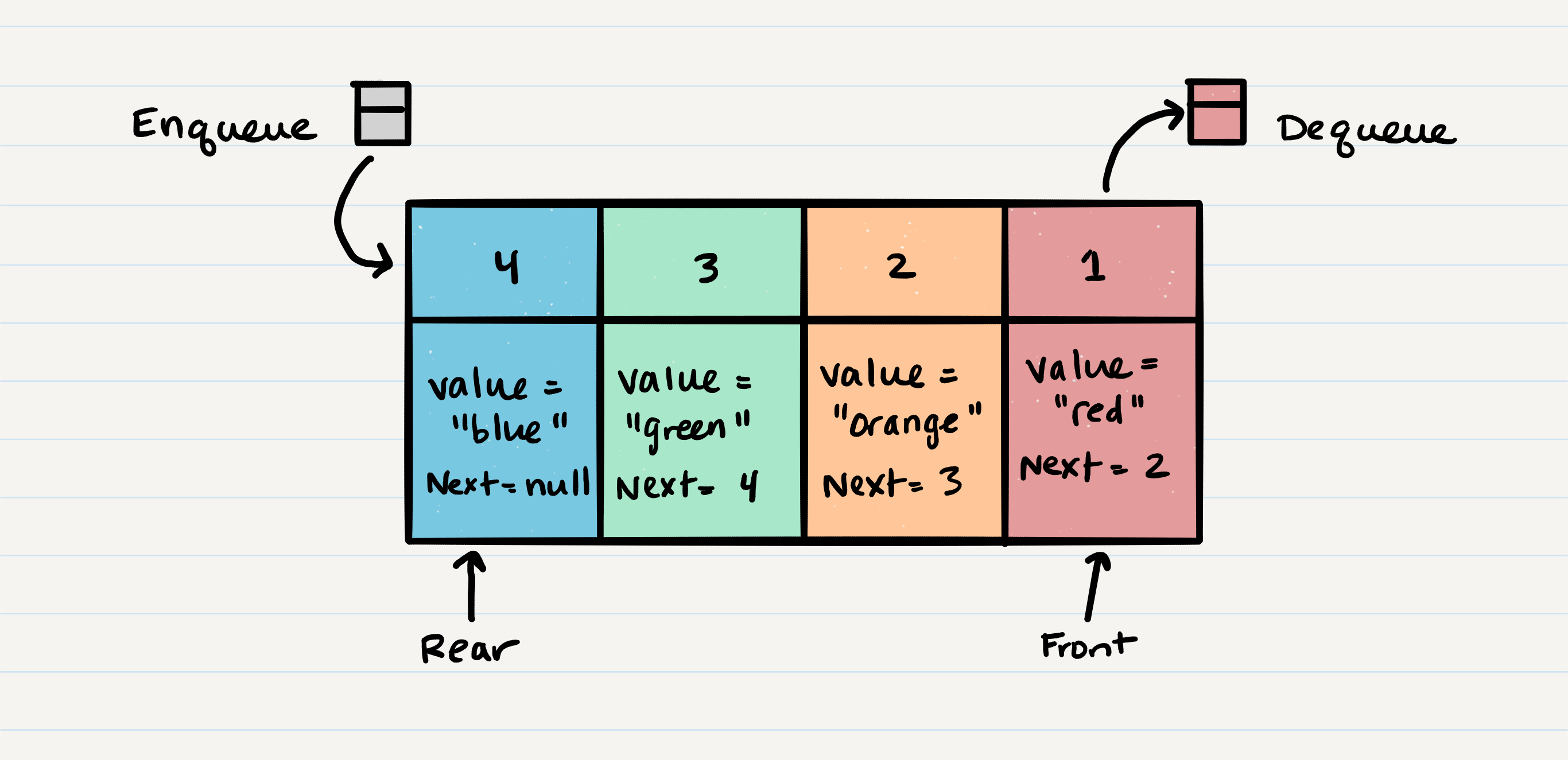
Queue Visualization
the following picture shows the structure of a queue
Queue methods and operations
- Enqueue: add nodes to the queue
- Dequeue: remove nodes from a queue
- Front: first Node of the queue.
- Rear: last Node of the queue.
- Peek: the value inside the first node in a queue
- IsEmpty: returns true when queue is empty otherwise returns false.
Enqueue and Dequeue
these two methods will always have a constant time complexity because you will always add or remove the first node .
ALGORITHM enqueue(value)
// INPUT <-- value to add to queue (will be wrapped in Node internally)
// OUTPUT <-- none
node = new Node(value)
rear.next <-- node
rear <-- node
ALGORITHM dequeue()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- value of the removed Node
// EXCEPTION if queue is empty
Node temp <-- front
front <-- front.next
temp.next <-- null
return temp.value
### Peek
-
When conducting a peek, you will only be inspecting the front Node of the queue.
-
Typically, you want to check isEmpty before conducting a peek. This will ensure that an exception is not raised.
-
big O of time for peek is O(1) // constant
ALGORITHM peek()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- value of the front Node in Queue
// EXCEPTION if Queue is empty
return front.value
IsEmpty
Time complexity // O(1)
ALGORITHM isEmpty()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- boolean
return front = NULL
Applications of Queue Data Structure
- When a resource is shared among multiple consumers.
- When data is transferred asynchronously (data not necessarily received at same rate as sent) between two processes. 3) In Operating systems:
4) In Networks:
a) Queues in routers/ switches
b) Mail Queues
5) Variations