reading-notes
Linear Regressions
The term “linearity” in algebra refers to a linear relationship between two or more variables.
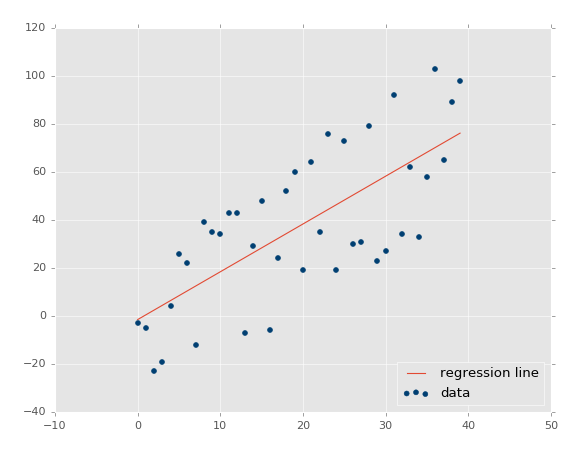
Linear regression performs the task to predict a dependent variable value (y) based on a given independent variable (x). So, this regression technique finds out a linear relationship between x (input) and y(output). Hence, the name is Linear Regression. If we plot the independent variable (x) on the x-axis and dependent variable (y) on the y-axis, linear regression gives us a straight line that best fits the data points, as shown in the figure below:
Boston Housing Data Set
This data set is available in sklearn Python module, so it could be accessed using scikitlearn. It can be imported Boston data set into Ipython notebook and store it in a variable called boston.

Scikit Learn
Now, we are going to fit a linear regression model and predict the Boston housing prices.
consider:
Y = boston housing price(also called “target” data in Python)
and
X = all the other features (or independent variables)
linear regressions can be imported as:

Important functions to keep in mind while fitting a linear regression model are:
lm.fit()-> fits a linear modellm.predict()-> Predict Y using the linear model with estimated coefficientslm.score()-> Returns the coefficient of determination (R^2). A measure of how well observed outcomes are replicated by the model, as the proportion of total variation of outcomes explained by the model.- .coef_ gives the coefficients and .intercept_ gives the estimated intercepts.
Predicting Prices
I am going to calculate the predicted prices (Y^i) using lm.predict. Then I display the first 5 housing prices. These are my predicted housing prices.
lm.predict(x)[0:5]
Then I plot a scatter plot to compare true prices and the predicted prices.


Residual Plots
Residual plots are a good way to visualize the errors in your data. If you have done a good job then your data should be randomly scattered around line zero. If you see structure in your data, that means your model is not capturing some thing. Maye be there is a interaction between 2 variables that you are not considering, or may be you are measuring time dependent data.

Multiple linear regression
Multiple linear regression attempts to model the relationship between two or more features and a response by fitting a linear equation to the observed data.
Assumptions:
Given below are the basic assumptions that a linear regression model makes regarding a dataset on which it is applied:
- Linear relationship: Relationship between response and feature variables should be linear.

-
Little or no multi-collinearity: It is assumed that there is little or no multicollinearity in the data. Multicollinearity occurs when the features (or independent variables) are not independent of each other.
- Little or no auto-correlation: Another assumption is that there is little or no autocorrelation in the data. Autocorrelation occurs when the residual errors are not independent of each other.
- Homoscedasticity: describes a situation in which the error term (that is, the “noise” or random disturbance in the relationship between the independent variables and the dependent variable) is the same across all values of the independent variables.

Applications of linear regression:
- Trend lines
- Economics
- Finance
- Biology