reading-notes
State and Props
React: Component Lifecycle Events
Component lifecycle events are The methods that you are able to use on react components whether they are classes or functions
These methods can be called during the lifecycle of a component, and they allow you to update the UI and application states, there are 3 phases of this lifecycle which are:
Mounting
When an instance of a component is being created and inserted into the DOM it occurs during the mounting phase. Constructor, static getDerivedStateFromProps, render, componentDidMount, and UNSAFE_componentWillMount all occur in this order during mounting.
Updating
Anytime a component is updated or state changes then it is rerendered. These lifecycle events happen during updating in this order:
static getDerivedStateFromProps
shouldComponentUpdate
render
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
componentDidUpdate
UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps
Unmounting
The final phase of the lifecycle if called when a component is being removed from the DOM. componentWillUnmount is the only lifecycle event during this phase.
constructor()
The constructor for a React component is called before it is mounted. Example:
class FishTableRow extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super(props); //gives us access to props
//Don’t call this.setState() here
this.state = { //intitialize local state
showDescription: false
}; }
**Avoid using this.setState() in the constructor because it can lead to side effects, and it is unnecessary. **
static getDerivedStateFromProps()
This method exists for rare cases where the state relies on changes in props over time.
render()
Render is the only required method in a class component. It will examine this.Example:
ReactDOM.render(
<FishTable fishes= {fishData}/>,//set fishes
document.getElementById(‘app’)
);
componentDidMount()
This method is invoked immediately after a component is mounted. If you need to load anything using a network request or initialize the DOM, it should go here.
Here we use componentDidMount() to connect to the YouTube API and get videos when the components is rendered.
componentDidMount() {
console.log(‘got videos’);
this.getVideos(‘cats’);
}
getVideos(query) {
var options = {
key: this.props.YOUTUBE_API_KEY,
query: query
};
shouldComponentUpdate()
The default behavior in react is to rerender after every state change.
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
This is another rarely used method that allows you to capture a picture of the DOM to check it before actually changing anything on the DOM.
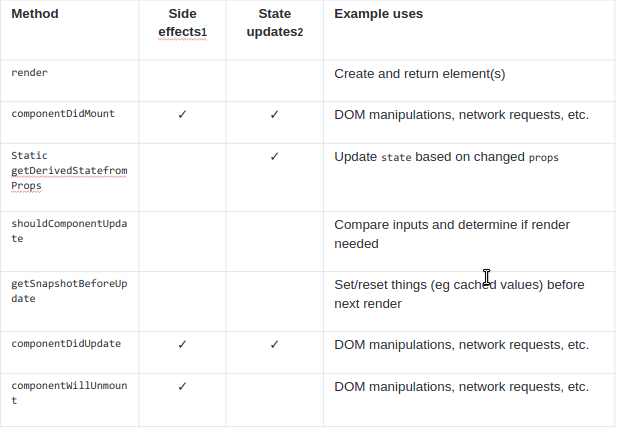
Here is a chart to help you keep track of the lifecycle events :
React Bootstrap
React Bootstrap is :
Rebuilt with React
React-Bootstrap replaces the Bootstrap JavaScript. Each component has been built from scratch as a true React component, without unneeded dependencies like jQuery.
Bootstrap at its core
Built with compatibility in mind, we embrace our bootstrap core and strive to be compatible with the world’s largest UI ecosystem.
Accessible by default
The React component model gives us more control over form and function of each component.